ALLERGY PART 1
What is the familial risk factors of allergy?
The risk of allergic disease in a child approaches 50% when 1 parent is allergic and
66% when both parents are allergic, with maternal history of atopy having a
greater effect than paternal history.
What is allergic salute?
Because of nasal pruritus and rhinorrhea, children with allergic rhinitis often rub their nose upward with the palm of their hand. This repeated maneuver may give rise to the nasal crease , a horizontal wrinkle over the bridge of the nose.
Characteristic vigorous grinding of the eyes with the thumb and side of the fist is frequently observed in children with allergic conjunctivitis.
What is allergic cluck?
The allergic cluck is produced when the tongue is placed against the roof of the mouth to form a seal and withdrawn rapidly in an effort to scratch the palate.
What are allergic shiners?
Parents are often concerned about blue-gray to purple discolorations beneath their child's lower eyelids, which can be attributed to venous stasis and are referred to as allergic shiners.
They are found in up to 60% of allergic patients and almost 40% of patients without allergic disease. Thus,“shiners” may suggest, but are not diagnostic of, allergic disease.
What are Dennie Morgan folds?
Dennie-Morgan folds (Dennie lines) are a feature of atopic dermatitis. These are prominent infraorbital skin folds that extend in an arc from the inner canthus beneath and parallel to the lower lid margin.
What is lip lickers dermatitis?
cheilitis caused by drying of the lips from continuous mouth breathing or repeated licking of the lips in an attempt to replenish moisture and relieve discomfort (lip licker's dermatitis ).
What are the skin manifestations of allergy?
Xerosis, Keratitis pilaris, thickening of palms and soles and exaggerated palmar and plantar creases(hyperlinearity).
What is keratitis pilaris?
It is a benign condition characterized by skin-colored or slightly pink papules caused by
keratin plugs lodged in the openings of hair follicles. It is often found in facial cheel and extensor surfaces of arms and thighs.
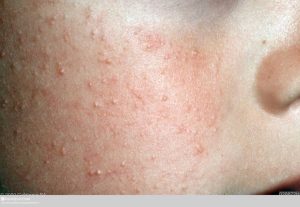
What is allergic gap?
Continuous open-mouth breathing with chapped lips.
Can age help us in identifying type of allergen?
The age of the patient is an important consideration in identifying potential allergens. Infants and young children are first sensitized to allergens that are in their environment on a continuous basis, such as dust mites, animal dander, and fungi.
Sensitization to seasonal allergens usually takes several seasons ofexposure to develop and is thus unlikely to be a significant trigger of symptoms in infants and toddlers.
Which allergy is most common in infants and younger children?
Food allergies are more common in infants and young children, resulting primarily in cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and, less frequently, respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms.
What are ear findings in allergic conditions?
The external ear should be examined for eczematous changes in patients with
atopic dermatitis, including the postauricular area and base of the earlobe.
Also, otitis media with effusion is common in children with allergic rhinitis.
What is the most common hematological abnormality associated with allergy?
Peripheral blood eosinoplilia i.e presence of >500 eosinophils/μL in peripheral blood.
Apart from blood eosinophilia Nasal and bronchial secretions may be examined for the presence of
eosinophils.
The presence of eosinophils in the sputum of asthmatic patients is classic.
An increased number of eosinophils in a smear of nasal mucus with Hansel stain is a more sensitive indicator of nasal allergies than peripheral blood eosinophilia and can aid in distinguishing allergic rhinitis from other causes of rhinitis.
What other blood tests can help in establishing the diagnosis of allergy?
IgE levels.
IgE is the primary antibody associated with immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
IgE values are measured in international units (IU), with 1 IU equal to 2.4 ng of IgE.
IgE levels are highest in which of the allergic conditions?
atopic dermatitis tend to have the highest levels, whereas patients with allergic asthma generally have higher levels than those with allergic rhinitis.
What is the problem with IgE levels in diagnosis of allergy?
Poor diagnostic value as approximately half of patients with allergic disease have total IgE levels in the normal range.
What is sIgE?
Allergen specific IgE. The presence of IgE specific for a particular allergen can be documented in
vivo by skin testing or in vitro by the measurement of allergen-specific IgE (sIgE) levels in the serum.
What is in vivo allergic testing?
Allergen skin testing is the primary in vivo procedure for the diagnosis of allergic disease.
What is the principle behind the allergic skin test?
Mast cells with sIgE antibodies attached to high-affinity receptors on their surface reside in the skin of allergic patients.
When a minute amount of an allergen into the skin of the sensitized patient cross-linking of IgE antibodies on the mast cell surface occurs triggering local mast cell activation.
The activated, these mast cells release a variety of preformed and newly generated mediators that act on surrounding tissues.
Histamine is the mediator most responsible for the immediate wheal and flare
reactions observed in skin testing.
Examination of the site of a positive skin test result reveals a pruritic wheal surrounded by erythema. The time course of these reactions is rapid in onset, reaching a peak within 10-20 min and usually
resolving over the next 30 min.
How skin prick-puncture test done?
A small drop of allergen is applied to the skin surface, and a tiny amount is introduced into the epidermis by lightly pricking or puncturing the outer layer of skin through the drop of extract with a small needle or other device.
A positive and negative control SPT, using histamine and saline, respectively, is performed with each set of skin tests.
A negative control is necessary to assess for dermatographism , in which reactions are caused merely by applying pressure to overly sensitive skin.
A positive control is necessary to establish the presence of a cutaneous response to histamine.
What is intradermal technique?
When the skin-prick test (SPT) result is negative but the history suggestive, selective skin testing (for vaccines, venom, drugs, and aeroallergens) using the intradermal technique may be performed.
This technique involves using a 26-gauge needle to inject 0.01-0.02 mL of an allergen extract diluted
1,000- to 10-fold into the dermis of the arm.
Can we perform food allergen testing using intradermal method?
Intradermal skin tests are not recommended for use with food allergens because of the risk of triggering anaphylaxis.
Irritant rather than allergic reactions can occur with intradermal skin testing if higher concentration is used.
Which is more sensitive ID test or skin prick test?
Although intradermal skin testing is more sensitive, positive SPT results tend to correlate better with clinical symptoms.
What are the effects of drugs in skin testing?
Medications with antihistaminic properties, in addition to adrenergic agents such as ephedrine and epinephrine, suppress skin test responses and should be avoided for appropriate intervals (approximately 5 half-lives) beforeskin testing.
Prolonged courses of systemic corticosteroids may suppress cutaneous reactivity by decreasing the number of tissue mast cells as well as their ability to release mediators.
The detection of presence of IgE either serologically or by skin testing denotes a sensitized state and is not equivalent to a clinical relevant allergic diagnosis. Sometimes a person has positive tests but no relevant clinical symptoms.
Also, the levels of IgE in blood or degree of wheal in skin doesnt corelate with disease severity.
Thus for diagnosis of allergy history is very important. Laboratory test provide support to the history.
Which is better serum sIgE or SPT?
Both are sensitive and have similar diagnostic properties.
The benefit of SPT is rapid diagnosis without venipuncture and low cost and that of serum sIgE is that performance is not limited by presence of skin disease (i.e., active atopic dermatitis) or medication use (i.e., antihistamines).
What are the provocation testing?
Provocation testing is performed to examine the association between allergen exposure and the development of symptoms.
e.g Bronchial provocation test using methacholine.
Oral food challenge
What is oral food challenge?
Oral food challenges are performed to determine whether a specific food causes symptoms or whether a suspected food can be added to the diet.
Food challenges are performed when the history and results of skin tests and immunoassays for sIgE fail to clarify the diagnosis of an allergy.
Although the double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge is currently the gold standard test for diagnosing food allergy, it is typically only performed in research studies due to the time and labor-intensive nature of this method.
How is it done?
It involves the ingestion of gradually increasing amounts of the suspected food at set intervals until the patient either experiences a reaction or tolerates a normal portion (i.e., 1 serving size) of the
food openly.

I am appreciative of this blog's ability to provide information on such an important subject. I discovered other segments here, and I'm excited to put these new instructions to use. allergic to ocean water
ReplyDeleteIt is truly a well-researched content and excellent wording. I got so engaged in this material that I couldn’t wait to read. I am impressed with your work and skill. Thanks. Read more info about allergy test prep
ReplyDelete