Congenital Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
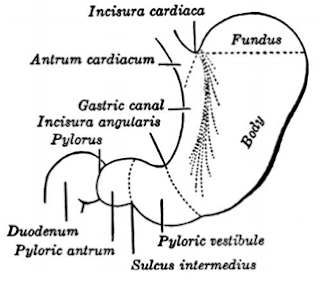
What are the parts of pylorus? The incisura angularis divides the stomach into a body to the left and a pyloric portion to the right. The sulcus intermedius further divides the pyloric portion of the stomach: the pyloric vestibule to the left, denoted by an outward convexity of the greater curvature. The pyloric antrum or pyloric canal to the right The pyloric antrum is 2.5 cm and terminates in pyloric orifice into duodenum. What happens to the normal anatomical structural in CHPS? In infants with IHPS, the pyloric ring is no longer identifiable as a clearly definable separation between the normally distensible pyloric antrum and the duodenal cap. Instead, a channel of variable length (1.5–2.0 cm) corresponding to the pyloric canal separates the normally distensible portion of the antrum from the duodenal cap. · Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis was first fully described by Harald Hirschsprung i...

Comments
Post a Comment